The oceanic heat budget is the result of heat gain and loss at any given site on the ocean surface. The ocean surface is the site of heat and energy exchange between the oceans and the atmosphere. The oceanic heat budget can be parameterized as:
- QI – insulation by sunlight:
- Length of day (latitude
- QLW – longwave radiation from sea
- Clouds, ice cover, waves,
- CO2, water temperature
- QS – sensible heat flux:
- Wind speed
- Air – sea temp. difference
- QL – latent heat flux: heat carried by evaporated water
- Increase with high wind and low humidity
- QV – heat transport by advection: currents
- General heat transport from southern to northern hemisphere
- Gulf Stream as central heater for northern Europe
- Oceans and atmosphere each transport ~½ of heat needed to warm higher latitudes
Height of sun (latitude, season, daytime
Clouds, dust, aerosols, waves
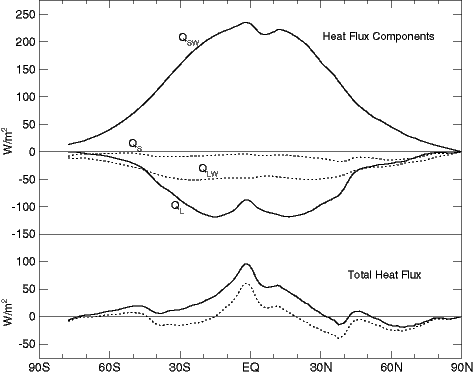
Upper: Zonal averages of heat transfer to and from the ocean; Lower:
Net heat flux through the sea surface
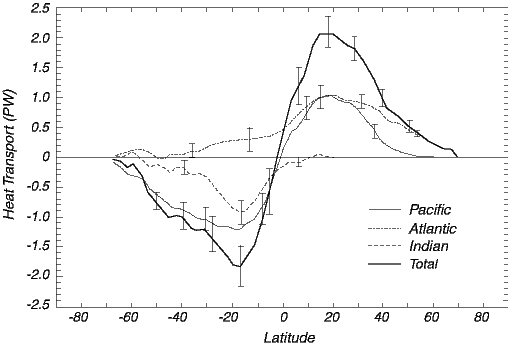
Northward heat transport for 1988 in each
ocean and the total transport summed over all oceans
The net heat loss from the oceans is largest in mid-latitudes and offshore of Japan and New England
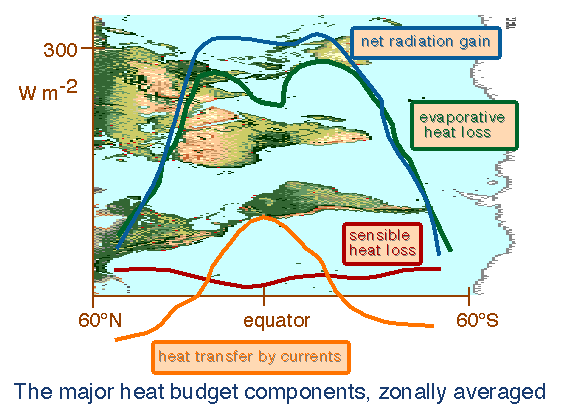
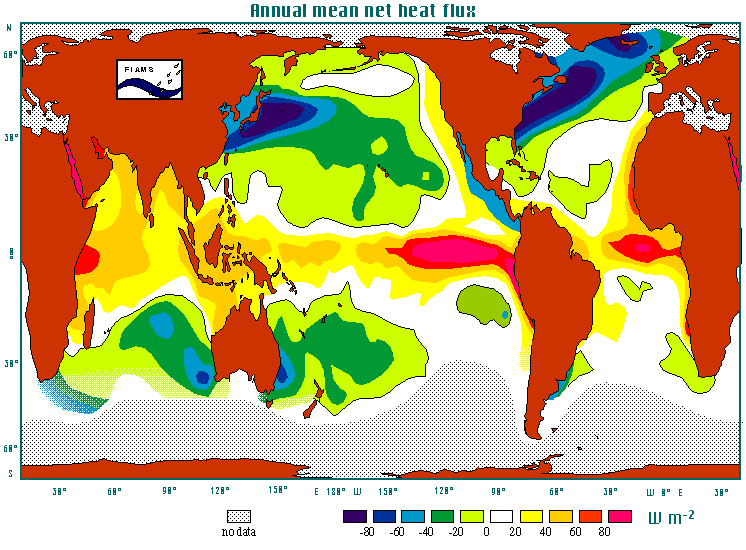
For more information see http://www.es.flinders.edu.au/~mattom/IntroOc/notes/lecture04.html