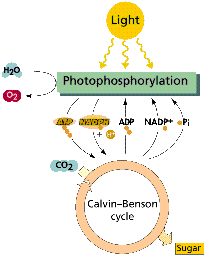
- The formation of organic matter from inorganic carbon (CO2) with light as the primary energy source
- 6 carbon dioxide + 6 water = 1 glucose + 6 oxygen
- Two reaction steps:
- (1) Light reaction: photophosphorylation: production of O2 and energy from H2O
- (2) Dark reaction: carbon fixation: CO2 to glucose
6 CO2 + 6 H20 = C6H12O6 + 6 O2
(Where does the O2 come from, H2O / CO2?)
- Phytoplankton and algal photosynthesis = primary production
- Organisms that perform photosynthesis = primary producers = autotrophic = phototrophic organisms
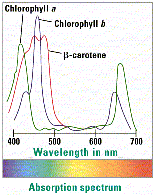
- All phototrophic organisms possess chlorophyll a and several accessory pigments (chl. b, c, carotenoids), which serve as antenna pigments to capture light energy and transfer electrons to the photosynthetic reaction center
- Each pigment has a distinct absorption spectrum
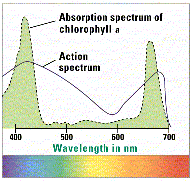
- Photosynthesis most efficient in blue and red light, according to absorption maximum of chlorophyll (action spectrum)
- P vs. I curves (photosynthesis versus light intensity): shows photosynthetic adaptation
- Gross production = total production; net production = gross prod. – respiration
- Compensation point: photosynthesis = respiration,
- Pmax = maximum production; depends on dark reaction (unlimited growth) or limiting resources
- Initial slope a: photosynthetic efficiency (how good is low light used), also quantum yield f = DP/DI; depends on light reaction
- Ik: summarizes key characteristics Pmax and a in one term; shade-adapted cells have lower Ik than high-light cells
net production = 0
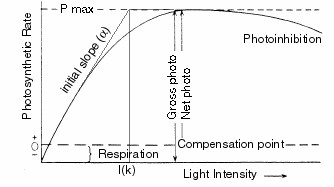
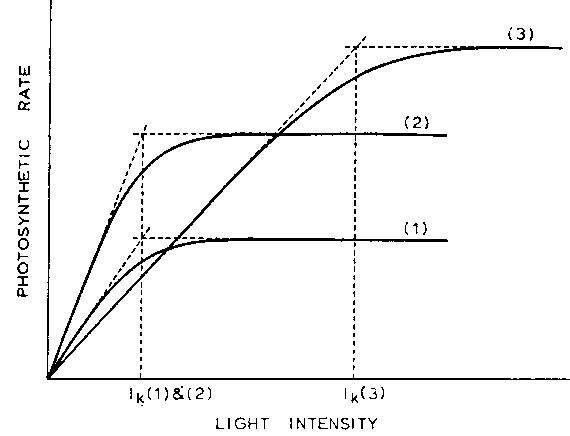
Note: Species (1) and (2) have the same Ik despite different
Pmax and a. The lower Ik
of (1) and (2) as compared to (3) reveals them as shade-adapted species.
Sverdrup's Model of Critical Depth
- Photosynthesis decreases exponentially with depth due to decrease in light availability
- Respiration is unaffected by light and remains constant with depth
- Phytoplankton is mixed by turbulence and experiences different light intensities over time, sometimes above and sometimes below compensation point
- Critical depth = depth at which photo-synthesis of the total water column phytoplankton population equals their total respiration
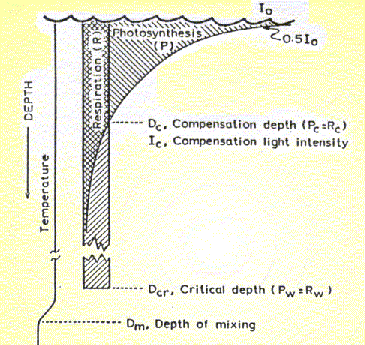
A phytoplankton population can only proliferate if mixing is shallower than the critical depth. Only then is the population net production >0