- Estuaries are among the most productive marine ecosystems with high biomass of benthic algae, seagrass and phytoplankton
- Nutrients are imported from land, but also retained within the estuary
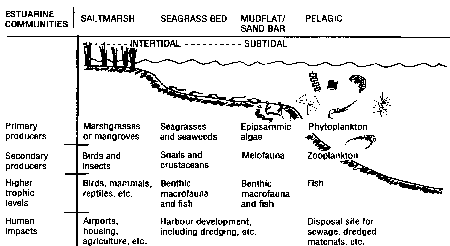
- Sequence of communities: saltmarsh, seagrass bed, mudflat/sand, pelagic
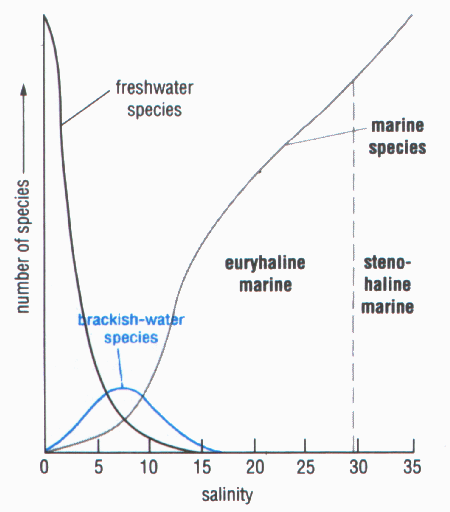
- Salinity gradient: mixture of freshwater and marine organisms, only few real brackish-water species; diversity lowest in brackish water (5-10‰)
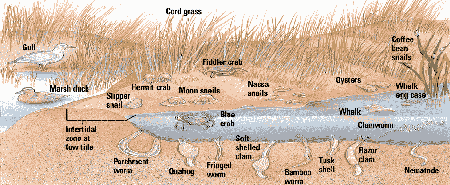
- Dominated by marshgrasses (flow- ering plants) as high as 2 m, which trap nutrient-rich sediments
- most plant tissues are not grazed but get into detrital food web
- slow decay and deep sediment, saltmarshes growh upwards, eventually filling the estuary and becoming land
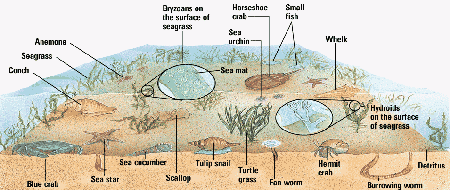
- Eelgrass (temperate) and Turtlegrass (tropical)
- few seaweeds, which do not grow well on muddy sediment
- many epiphytic diatoms on seagrass contribute to primary production and serve as food for snails
- habitat for sessile animals (hydroids)
- seagrass biomass ends up in detritus
- manatees and sea turtles graze Turtlegrass
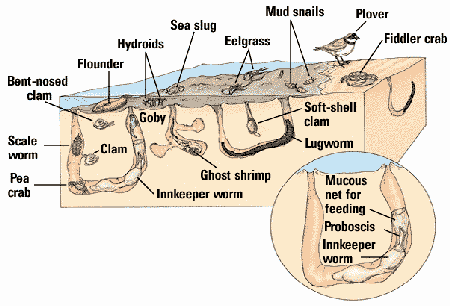
- Primary producers: epipsammic algae, mostly benthic diatoms and dinoflagellates
- cyanobacteria mats on mudflats
- production 10% or less of seagrass beds and saltmarshes, decreasing with grain size of sediment (mud more productive than sand)
- macro- and meiobenthos, often detrivores, living of deposits from seagrasses and marshes
- birds important grazers
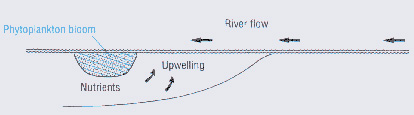
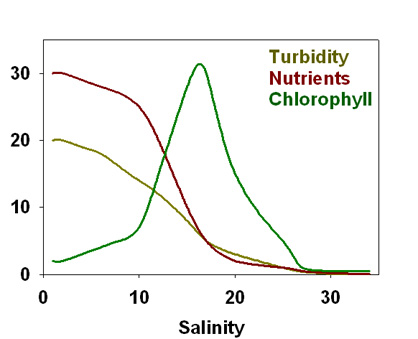
- High production by nutrients imported by the freshwater inflow
-
Highest production and
biomass at intermediate salinities. At head of estuary, nutrient concentrations are high
but turbidity by sediments suspended in river water is high as well so that phytoplankton
remains light-limited; as sediments sink out of the water column along the river plume and
water turbidity decreases, phytoplankton can make use of high nutrient concentrations at
intermediate salinities.
- benthic filter-feeders profit from plankton production
- high sedimentation of plankton from estuarine plumes can cause oxygen consumption and anoxic sediments at the seaward edge (even hypoxia in the water; for example Mississippi River plume)
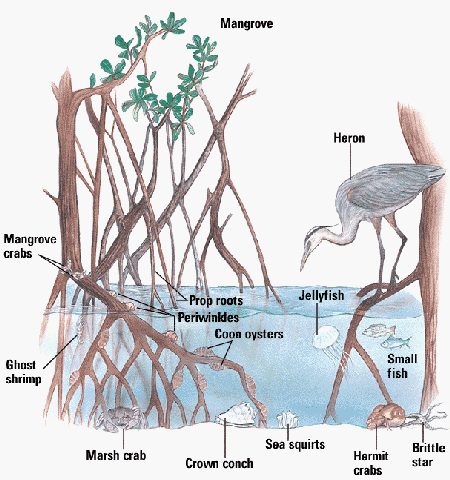
- Mangroves replace saltmarshes in tropical regions (60-75% of tropical and subtropical coastlines), upper tidal zone
- High salinity tolerance: broad distribution from high in the estuary to almost fully marine water, but wave-protected zone
- Mangroves: 12 genera, 60 species of flowering, terrestrial trees and shrubs restricted to mangrove swamps; shallow and far-reaching roots; airial roots help in oxygen supply because the sediments are anoxic;
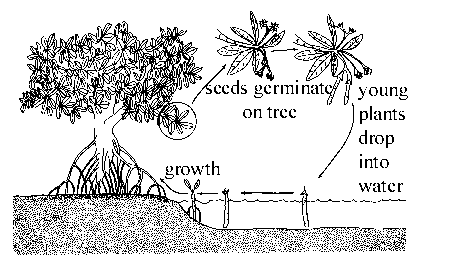
- Viviparous growth: seeds germinate on the tree, and young plants fall into the water
- Ecological importance:
- Host and feed breeding birds
- protect shoreline from erosion during tropical storms
- important fisheries and supply (boat and fire wood) in native people
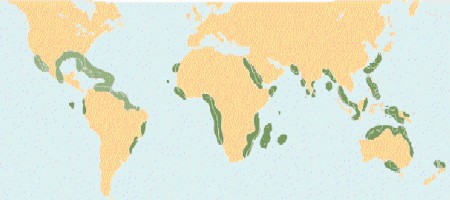
The distribution of mangroves: