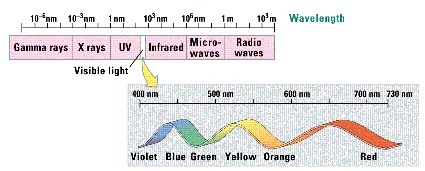
- 280 – 320 nm: UV-B (harmful)
- 320 – 400 nm: UV-A
- 400 – 700 nm: PAR – Photosynthetically Active Radiation
- > 700 nm: IR (Infrared Radiation)
- Units of light (irradiance):
- Photon flux: mmol photons m-2 s-1 = mE m-2 s-1 (Einstein)
- Energy: W m-2
- Maximum surface irradiation is typically less than 2000 mE m-2 s-1 on bright day
- Blue light contains more energy per photon than red light; therefore units of Watt and Einstein cannot easily be converted into each other. For conversion, average energy content of 550 nm light (green) is used.
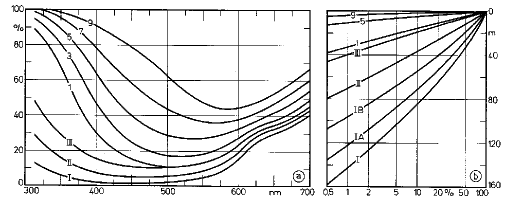
- Light decreases exponentially with depth
- Blue light penetrates deepest into the ocean, red light is absorbed fastest (Consequences: Live seems more ‘colorless’ with depth)
- Optical classes of water (Jerlov):
- Coastal oceans: stronger light absorption, brownish to greenish due to shift in spectral absorbance
- Open oceans: clearest water, deep euphotic zone, blue color
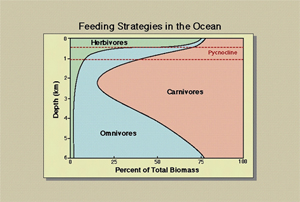
- Light penetrates only down to 100-200 m depth
- Herbivores, which feed on phytoplankton, are restricted to the euphotic zone
- Carnivores, which feed on zooplankton, thrive in mid-waters
- Omnivores, which eat both living prey and dead material (fecal pellets, dead organisms) thrive in the deep-sea
Horizontal distribution of zooplankton